Customer Feedback FAQ Hub
Strategies to collect, analyze, and act on insights to fuel innovation.
Customer feedback is a powerful organizational tool—capable of sustaining a company and fueling its future innovation. But its impact depends on how thoughtfully it’s collected, how systematically it’s analyzed, and how intentionally it’s acted upon. In this FAQ, feedback expert Cameron Conaway answers the most common (and emerging) questions leaders ask.
Collecting Customer Feedback
What is customer feedback?
Customer feedback is the information customers share—directly or indirectly—about their experience with a product, service, or brand. It includes opinions, preferences, complaints, compliments, and suggestions.
Every piece of feedback is a data point that can inspire innovation. Watch how Slack leveraged this:
Why is customer feedback important to business success?
Customer feedback drives improvement, innovation, and retention. It helps identify issues early, reveals what is working, and builds customer trust. Research shows that even online reviews can fuel product iteration and innovation.
However, much of it goes unseen. Watch this short video on feedback visibility:
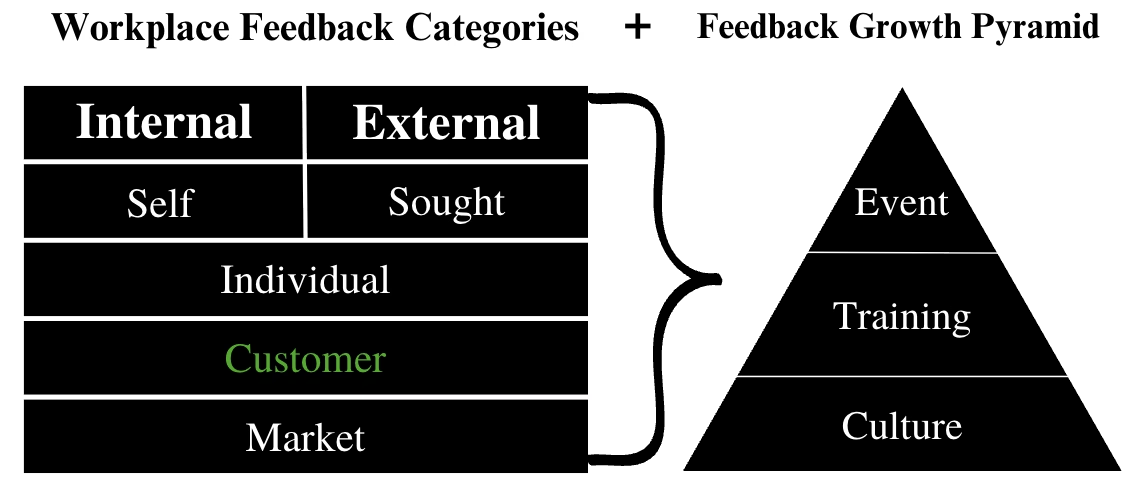
What are the different types of customer feedback?
Feedback can be grouped by collection method (Solicited vs. Unsolicited), format (Structured/Ratings vs. Unstructured/Comments), and tone (Positive, Negative, Constructive).
What are the best channels for collecting customer feedback?
- Surveys: Email, SMS, or in-app.
- In-app feedback tools: Real-time insights (e.g., Pendo, Qualaroo).
- Customer interviews: Rich, story-driven insight.
- Public reviews: Trustpilot, G2, Yelp.
- Social listening: Brand mentions on social media.
- Support interactions: Support tickets and chats.
Example: See how Qualaroo and Hootsuite use feedback channels:
What’s the best way to ask for customer feedback?
Requests should be personalized, specific, optional, and timed right (immediately after a relevant interaction). For example: “Hi Alex, thanks for using our dashboard today. Could you take 15 seconds to let us know how it went?”
What’s the difference between solicited and unsolicited feedback?
Solicited feedback is requested by you (surveys, NPS). Unsolicited feedback is offered freely by the customer (social posts, reviews). Innovation often hides in the unsolicited feedback because it reveals what customers care about most, not just what you asked about.
Example: How a local restaurant handled unsolicited negative feedback:
What are some good examples of customer feedback?
Good feedback is specific and actionable. E.g., “It took me four clicks to find the billing page—felt buried.” This is more useful than generic complaints because it points to a solution.
What’s the best time to collect customer feedback?
Timing matters. Collect immediately after interactions (support chat), at key milestones (30 days post-purchase), or following success signals (completing a workflow).
How can organizations collect feedback at scale?
Use automation, centralize data streams, use integrations (Zapier, etc.), and establish “feedback moments” in workflows. Check out how Microsoft captures feedback at scale:
What are the best tools for collecting customer feedback?
Top tools include Typeform/SurveyMonkey (Surveys), Pendo/Qualaroo (In-App), Qualtrics/Medallia (Voice of Customer), and Hootsuite (Social Listening).
Tool Example: Qualtrics and ServiceNow:
Analyzing Customer Feedback
What is a customer feedback system?
It is the end-to-end process to Collect, Classify, and Communicate feedback. A great system isn’t just about data—it’s about decisions.
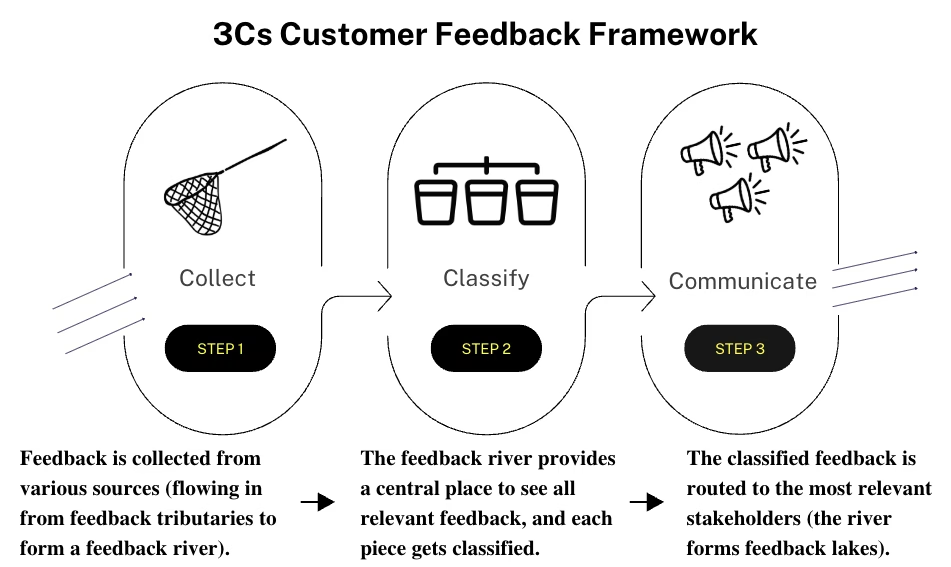
What are feedback rivers, tributaries, and lakes?
Metaphors for feedback flow: Rivers are major streams (reviews, support tickets). Tributaries are smaller sources (social mentions). Lakes are where insights are stored (CRM, dashboard). Great organizations build ecosystems, not just pools.
How should we organize and classify feedback?
Design a taxonomy: sort by Theme (product, pricing), Sentiment (positive/negative), Urgency, and Frequency. Consider using the A.C.A.F. model:
What’s the role of AI in analyzing customer feedback?
AI accelerates processing via sentiment analysis, topic detection, and auto-tagging. It helps handle scale but should be an assistant, not a replacement for human judgment. Example: AWS LLM models:
How do we reduce bias in feedback analysis?
Ask inclusive questions, capture diverse voices (not just power users), and use multiple analysts. Watch out for systemic bias where feedback only comes from one region.
What metrics should we track?
Key metrics include NPS (Net Promoter Score), CSAT (Customer Satisfaction), and CES (Customer Effort Score). Honda provides a great example of reporting on these:
What’s the difference between NPS, CSAT, and CES?
| Metric | Question | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| NPS | “How likely are you to recommend us?” | Loyalty & Brand |
| CSAT | “How satisfied were you?” | Support & Product |
| CES | “How easy was it?” | Usability & Friction |
Acting on Customer Feedback
What does it mean to close the feedback loop?
It means responding to feedback to show you’ve heard it and taken action. Acknowledge, share context, take action, and follow up. See how RedHat does it:
How can we turn feedback into product improvements?
Centralize feedback for product teams, tag by feature, look for patterns across personas, and prioritize using frameworks like RICE. Keep a “customer feedback changelog” to build trust.
How do we prioritize customer feedback?
Filter by Impact (severity/volume) and Effort (cost/time). Use the Kano Model (basic needs vs delighters) or RICE scoring. Always align prioritization with company strategy.
How do we handle negative feedback posted publicly?
Acknowledge quickly, stay calm, take it offline if needed, and follow up publicly once resolved. A handled complaint can become a brand asset.
How do we respond to anonymous customer feedback?
Treat it seriously. Look for trends. Acknowledge it publicly (e.g., in newsletters) to show you are listening even if you can’t reply directly. Anonymous feedback often reveals blind spots.
Leading with Customer Feedback
What is feedback-led innovation?
It is using customer insights to start and guide the lifecycle of new features or business models. Companies like Slack and Canva grew rapidly by co-creating solutions with users.
How do we create a culture of acting on feedback?
Model it from the top, make feedback visible in all-hands meetings, celebrate action, and bake it into processes like sprint reviews. You need a culture that prioritizes listening.
What’s the difference between customer service and customer feedback?
| Aspect | Customer Service | Customer Feedback |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Resolution (Reactive) | Improvement (Proactive) |
| Timing | After issue arises | Ongoing |
Great organizations use service interactions to generate feedback, and feedback to improve service.
How do we align teams around customer feedback?
Create shared dashboards, assign owners to themes, and integrate feedback into team KPIs. Alignment isn’t just access—it’s accountability.
How do we train employees to engage with feedback?
Start with mindset (feedback isn’t judgment), roleplay scenarios, use frameworks like SBI™, and encourage reflection on how feedback shaped past decisions.
What’s the future of customer feedback?
Real-time, in-context capture, AI-assisted analysis, and predictive loops. Feedback will move from a “feature” to a competitive advantage for innovation.
Feedback is fuel for innovation.
Get Cameron’s free guide here. It includes the complete breakdown of feedback definitions, types, and examples in one easy-to-navigate PDF. Perfect for printing, sharing with your team, or keeping as a quick reference.
↓ Download the PDF